We've been talking about it for a while now, composting will become compulsory from January 1, 2024 . Indeed, each household, industrialist and community will have the obligation to sort their food waste and green garden waste so that they can be used as composting solutions. This measure is part of the AGEC law, relating to the fight against food waste and the circular economy.
At a time when environmental preservation is at the heart of global concerns, France is taking a further step towards a more sustainable future with this law.
You certainly have a lot of questions about this new law and you may also have concerns about its implementation or facing possible fines if you do not respect it. We are here to answer together any questions you may have.

New law on composting in 2024:
The new law is based on 5 main axes :
- Get rid of disposable plastic
- Better inform consumers
- Fight against waste and for solidarity reuse
- Acting against planned obcolescence
- Produce better
Many municipalities offer subsidies or composters at reduced prices to encourage the implementation of this measure. Do not hesitate to contact yours to find out what is in place if you wish to have your own composter at home.

Why switch to compost?
Composting is a significant contribution to preserving the environment. We give you some reasons why composting is beneficial:
- Waste reduction : by composting organic waste such as kitchen scraps, fruit and vegetable peelings, garden waste, you reduce the amount of waste that will be sent to landfill.
Did you know that 26% of our gray bins are filled with food waste which will be incinerated or buried?
- Soil enrichment : Compost is rich in nutrients and by adding it to your garden you improve the structure of the soil and increase its water retention capacity. The compost will act as an organic fertilizer, eliminating the need for chemical fertilizers.
- Water conservation : as said before, soils enriched with compost have better water retention. As a result, it reduces the need for irrigation and is crucial in drought-prone regions.
- Reduction of carbon footprint : by reducing waste sent to landfill, this reduces methane emissions (a powerful greenhouse gas) produced during the decomposition of organic waste.
- Energy saving : waste collection, transportation and management represent a huge energy expenditure. By composting directly at home, you reduce the quantity of waste to be processed and at the same time energy consumption.
In summary, composting is a simple action to implement at home, but which has a huge impact on the environment. In addition, you educate your children about positive actions for a more sustainable future.

What is the principle of compost?
Compost is the result of a fermentation of organic or plant waste, thus obtaining a natural fertilizer for plants and soil.
The compost can be used once it no longer smokes and has become brown and grainy with an earthy smell. At this stage we can no longer recognize the original elements.
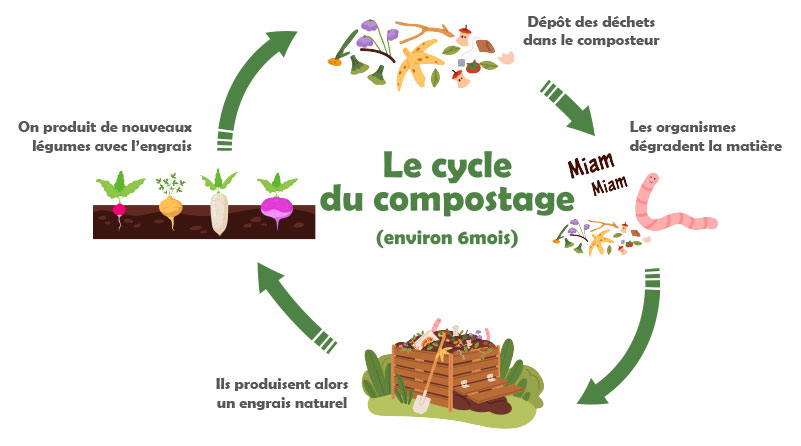

How to compost properly?
Composting is not very complicated in itself, provided you follow certain rules. Indeed, piling up organic waste at the bottom of your garden is not enough to create compost. You still need to know what you can put and what you should avoid putting in your composting bin.
First of all, you must place your composter in a shaded place and it must be in contact with the soil of your garden. Insects, earthworms and bacteria will be able to nestle in the compost. They will promote aeration of your compost, degrade waste and improve the quality of the compost.
Then make successive layers of fresh elements (peeings, grass clippings, etc.) and carbonaceous elements (dead leaves, plants, etc.). The compost should be neither too wet nor too dry.
A little advice: do not put waste that could attract dogs and cats on the surface of the compost.
If composting is carried out in good balanced conditions (heat, ventilation, humidity), you will be able to use your compost within six months to a year to enrich your vegetable patch, flowers or garden with a completely natural fertilizer!
In your composter, you can put:
- Your kitchen waste : fruit and vegetable peelings, cheese rinds, leftover meals, coffee grounds, filters, tea bags, crushed egg shells, stale bread, etc.
- Your garden waste : grass clippings, weeds, wilted flowers, dead leaves, small branches, etc.
- Your household waste : paper towels, paper tissues, unprinted cardboard boxes, etc.
By mixing all these types of organic or household waste, dry or wet, you will optimize the compost manufacturing process. You will have quality compost and it will take less time to form.


What I should not put in my compost:
As stated just above, your composter needs several things in order to create quality compost. But there are things which, on the contrary, will cause your composter to lose its effectiveness, or even destroy it.
- In kitchen waste : leftover meat and fish, frying oils, kernels and shells of oilseeds, citrus peels, dairy products.
- In garden waste : large branches, sand, stones, gravel, waste treated with chemicals.
- In household waste : animal excrement, coal ashes, cigarette butts.

How to use your compost?
Compost is a real gold mine for your garden. There are several ways to use your compost once it is ready:
- Garden Fertilizer : Mix compost with your garden soil to enrich the soil with essential nutrients. This will promote plant growth and improve water retention.
- Mulch : Place a layer of compost around your plants as mulch. This will help retain moisture, control weeds and also regulate soil temperature.
- Fertilizer for potted plants : as for your garden, mix compost with the soil for your plants to provide it with nutrients.
- Soil activator : add compost to clay and heavy soils to improve their structure and drainage.
- For vegetables : add compost between the rows of vegetable plants to promote good harvests.
What can I compost?
Kitchen waste such as fruit and vegetable peelings, leftover meals, coffee grounds, etc. as well as garden waste such as cut grass, branches and dead leaves.
What should I compost?
Avoid leftover meats, dairy products, fats, large branches, animal droppings and diseased plants.
How long does it take to get compost?
It all depends on the conditions, but, in general, you have usable compost in a few months to a year.
Can I compost if I live in an apartment?
It is entirely possible to do this using special composters to compost indoors without having unpleasant odors.
How do I know if my compost is ready?
Compost that is mature will have a crumbly texture and a dark color as well as an earthy smell. At this stage, you can no longer recognize the original elements. And the compost no longer gives off smoke.
Does compost smell bad?
If it is carried out in good conditions, the compost does not give off any particular odor (except that of humus).





 By Cindy et Benoit
By Cindy et Benoit
